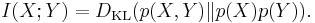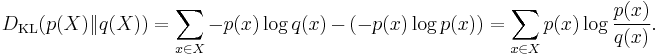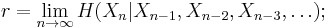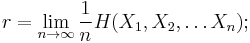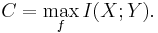Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and communicating data. Since its inception it has broadened to find applications in many other areas, including statistical inference, natural language processing, cryptography generally, networks other than communication networks — as in neurobiology,[1] the evolution[2] and function[3] of molecular codes, model selection[4] in ecology, thermal physics,[5] quantum computing, plagiarism detection[6] and other forms of data analysis.[7]
A key measure of information is known as entropy, which is usually expressed by the average number of bits needed to store or communicate one symbol in a message. Entropy quantifies the uncertainty involved in predicting the value of a random variable. For example, specifying the outcome of a fair coin flip (two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy) than specifying the outcome from a roll of a die (six equally likely outcomes).
Applications of fundamental topics of information theory include lossless data compression (e.g. ZIP files), lossy data compression (e.g. MP3s and JPGs), and channel coding (e.g. for Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)). The field is at the intersection of mathematics, statistics, computer science, physics, neurobiology, and electrical engineering. Its impact has been crucial to the success of the Voyager missions to deep space, the invention of the compact disc, the feasibility of mobile phones, the development of the Internet, the study of linguistics and of human perception, the understanding of black holes, and numerous other fields. Important sub-fields of information theory are source coding, channel coding, algorithmic complexity theory, algorithmic information theory, information-theoretic security, and measures of information.
Contents |
Overview
The main concepts of information theory can be grasped by considering the most widespread means of human communication: language. Two important aspects of a concise language are as follows: First, the most common words (e.g., "a", "the", "I") should be shorter than less common words (e.g., "benefit", "generation", "mediocre"), so that sentences will not be too long. Such a tradeoff in word length is analogous to data compression and is the essential aspect of source coding. Second, if part of a sentence is unheard or misheard due to noise — e.g., a passing car — the listener should still be able to glean the meaning of the underlying message. Such robustness is as essential for an electronic communication system as it is for a language; properly building such robustness into communications is done by channel coding. Source coding and channel coding are the fundamental concerns of information theory.
Note that these concerns have nothing to do with the importance of messages. For example, a platitude such as "Thank you; come again" takes about as long to say or write as the urgent plea, "Call an ambulance!" while the latter may be more important and more meaningful in many contexts. Information theory, however, does not consider message importance or meaning, as these are matters of the quality of data rather than the quantity and readability of data, the latter of which is determined solely by probabilities.
Information theory is generally considered to have been founded in 1948 by Claude Shannon in his seminal work, "A Mathematical Theory of Communication". The central paradigm of classical information theory is the engineering problem of the transmission of information over a noisy channel. The most fundamental results of this theory are Shannon's source coding theorem, which establishes that, on average, the number of bits needed to represent the result of an uncertain event is given by its entropy; and Shannon's noisy-channel coding theorem, which states that reliable communication is possible over noisy channels provided that the rate of communication is below a certain threshold, called the channel capacity. The channel capacity can be approached in practice by using appropriate encoding and decoding systems.
Information theory is closely associated with a collection of pure and applied disciplines that have been investigated and reduced to engineering practice under a variety of rubrics throughout the world over the past half century or more: adaptive systems, anticipatory systems, artificial intelligence, complex systems, complexity science, cybernetics, informatics, machine learning, along with systems sciences of many descriptions. Information theory is a broad and deep mathematical theory, with equally broad and deep applications, amongst which is the vital field of coding theory.
Coding theory is concerned with finding explicit methods, called codes, of increasing the efficiency and reducing the net error rate of data communication over a noisy channel to near the limit that Shannon proved is the maximum possible for that channel. These codes can be roughly subdivided into data compression (source coding) and error-correction (channel coding) techniques. In the latter case, it took many years to find the methods Shannon's work proved were possible. A third class of information theory codes are cryptographic algorithms (both codes and ciphers). Concepts, methods and results from coding theory and information theory are widely used in cryptography and cryptanalysis. See the article ban (information) for a historical application.
Information theory is also used in information retrieval, intelligence gathering, gambling, statistics, and even in musical composition.
Historical background
The landmark event that established the discipline of information theory, and brought it to immediate worldwide attention, was the publication of Claude E. Shannon's classic paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" in the Bell System Technical Journal in July and October 1948.
Prior to this paper, limited information-theoretic ideas had been developed at Bell Labs, all implicitly assuming events of equal probability. Harry Nyquist's 1924 paper, Certain Factors Affecting Telegraph Speed, contains a theoretical section quantifying "intelligence" and the "line speed" at which it can be transmitted by a communication system, giving the relation 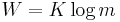 , where W is the speed of transmission of intelligence, m is the number of different voltage levels to choose from at each time step, and K is a constant. Ralph Hartley's 1928 paper, Transmission of Information, uses the word information as a measurable quantity, reflecting the receiver's ability to distinguish one sequence of symbols from any other, thus quantifying information as
, where W is the speed of transmission of intelligence, m is the number of different voltage levels to choose from at each time step, and K is a constant. Ralph Hartley's 1928 paper, Transmission of Information, uses the word information as a measurable quantity, reflecting the receiver's ability to distinguish one sequence of symbols from any other, thus quantifying information as 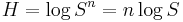 , where S was the number of possible symbols, and n the number of symbols in a transmission. The natural unit of information was therefore the decimal digit, much later renamed the hartley in his honour as a unit or scale or measure of information. Alan Turing in 1940 used similar ideas as part of the statistical analysis of the breaking of the German second world war Enigma ciphers.
, where S was the number of possible symbols, and n the number of symbols in a transmission. The natural unit of information was therefore the decimal digit, much later renamed the hartley in his honour as a unit or scale or measure of information. Alan Turing in 1940 used similar ideas as part of the statistical analysis of the breaking of the German second world war Enigma ciphers.
Much of the mathematics behind information theory with events of different probabilities was developed for the field of thermodynamics by Ludwig Boltzmann and J. Willard Gibbs. Connections between information-theoretic entropy and thermodynamic entropy, including the important contributions by Rolf Landauer in the 1960s, are explored in Entropy in thermodynamics and information theory.
In Shannon's revolutionary and groundbreaking paper, the work for which had been substantially completed at Bell Labs by the end of 1944, Shannon for the first time introduced the qualitative and quantitative model of communication as a statistical process underlying information theory, opening with the assertion that
- "The fundamental problem of communication is that of reproducing at one point, either exactly or approximately, a message selected at another point."
With it came the ideas of
- the information entropy and redundancy of a source, and its relevance through the source coding theorem;
- the mutual information, and the channel capacity of a noisy channel, including the promise of perfect loss-free communication given by the noisy-channel coding theorem;
- the practical result of the Shannon–Hartley law for the channel capacity of a Gaussian channel; as well as
- the bit—a new way of seeing the most fundamental unit of information.
Quantities of information
Information theory is based on probability theory and statistics. The most important quantities of information are entropy, the information in a random variable, and mutual information, the amount of information in common between two random variables. The former quantity indicates how easily message data can be compressed while the latter can be used to find the communication rate across a channel.
The choice of logarithmic base in the following formulae determines the unit of information entropy that is used. The most common unit of information is the bit, based on the binary logarithm. Other units include the nat, which is based on the natural logarithm, and the hartley, which is based on the common logarithm.
In what follows, an expression of the form 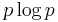 is considered by convention to be equal to zero whenever
is considered by convention to be equal to zero whenever 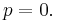 This is justified because
This is justified because 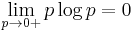 for any logarithmic base.
for any logarithmic base.
Entropy
The entropy, 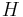 , of a discrete random variable
, of a discrete random variable  is a measure of the amount of uncertainty associated with the value of
is a measure of the amount of uncertainty associated with the value of  .
.
Suppose one transmits 1000 bits (0s and 1s). If these bits are known ahead of transmission (to be a certain value with absolute probability), logic dictates that no information has been transmitted. If, however, each is equally and independently likely to be 0 or 1, 1000 bits (in the information theoretic sense) have been transmitted. Between these two extremes, information can be quantified as follows. If  is the set of all messages
is the set of all messages 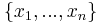 that
that  could be, and
could be, and 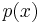 is the probability of
is the probability of  given some
given some 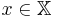 , then the entropy of
, then the entropy of  is defined:[8]
is defined:[8]
(Here, 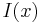 is the self-information, which is the entropy contribution of an individual message, and
is the self-information, which is the entropy contribution of an individual message, and 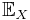 is the expected value.) An important property of entropy is that it is maximized when all the messages in the message space are equiprobable
is the expected value.) An important property of entropy is that it is maximized when all the messages in the message space are equiprobable  ,—i.e., most unpredictable—in which case
,—i.e., most unpredictable—in which case 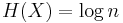 .
.
The special case of information entropy for a random variable with two outcomes is the binary entropy function, usually taken to the logarithmic base 2:
Joint entropy
The joint entropy of two discrete random variables  and
and  is merely the entropy of their pairing:
is merely the entropy of their pairing: 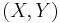 . This implies that if
. This implies that if  and
and 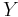 are independent, then their joint entropy is the sum of their individual entropies.
are independent, then their joint entropy is the sum of their individual entropies.
For example, if 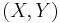 represents the position of a chess piece —
represents the position of a chess piece —  the row and
the row and 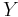 the column, then the joint entropy of the row of the piece and the column of the piece will be the entropy of the position of the piece.
the column, then the joint entropy of the row of the piece and the column of the piece will be the entropy of the position of the piece.
Despite similar notation, joint entropy should not be confused with cross entropy.
Conditional entropy (equivocation)
The conditional entropy or conditional uncertainty of  given random variable
given random variable 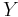 (also called the equivocation of
(also called the equivocation of  about
about 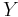 ) is the average conditional entropy over
) is the average conditional entropy over 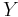 :[9]
:[9]
Because entropy can be conditioned on a random variable or on that random variable being a certain value, care should be taken not to confuse these two definitions of conditional entropy, the former of which is in more common use. A basic property of this form of conditional entropy is that:
Mutual information (transinformation)
Mutual information measures the amount of information that can be obtained about one random variable by observing another. It is important in communication where it can be used to maximize the amount of information shared between sent and received signals. The mutual information of  relative to
relative to 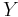 is given by:
is given by:
where 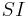 (Specific mutual Information) is the pointwise mutual information.
(Specific mutual Information) is the pointwise mutual information.
A basic property of the mutual information is that
That is, knowing Y, we can save an average of 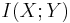 bits in encoding X compared to not knowing Y.
bits in encoding X compared to not knowing Y.
Mutual information is symmetric:
Mutual information can be expressed as the average Kullback–Leibler divergence (information gain) of the posterior probability distribution of X given the value of Y to the prior distribution on X:
In other words, this is a measure of how much, on the average, the probability distribution on X will change if we are given the value of Y. This is often recalculated as the divergence from the product of the marginal distributions to the actual joint distribution:
Mutual information is closely related to the log-likelihood ratio test in the context of contingency tables and the multinomial distribution and to Pearson's χ2 test: mutual information can be considered a statistic for assessing independence between a pair of variables, and has a well-specified asymptotic distribution.
Kullback–Leibler divergence (information gain)
The Kullback–Leibler divergence (or information divergence, information gain, or relative entropy) is a way of comparing two distributions: a "true" probability distribution p(X), and an arbitrary probability distribution q(X). If we compress data in a manner that assumes q(X) is the distribution underlying some data, when, in reality, p(X) is the correct distribution, the Kullback–Leibler divergence is the number of average additional bits per datum necessary for compression. It is thus defined
Although it is sometimes used as a 'distance metric', KL divergence is not a true metric since it is not symmetric and does not satisfy the triangle inequality (making it a semi-quasimetric).
Kullback–Leibler divergence of a prior from the truth
Another interpretation of KL divergence is this: suppose a number X is about to be drawn randomly from a discrete set with probability distribution p(x). If Alice knows the true distribution p(x), while Bob believes (has a prior) that the distribution is q(x), then Bob will be more surprised than Alice, on average, upon seeing the value of X. The KL divergence is the (objective) expected value of the Bob's (subjective) surprisal minus Alice's surprisal, measured in bits if the log is in base 2. In this way, the extent to which Bob's prior is "wrong" can be quantified in terms of how "unnecessarily surprised" it's expected to make him.
Other quantities
Other important information theoretic quantities include Rényi entropy (a generalization of entropy), differential entropy (a generalization of quantities of information to continuous distributions), and the conditional mutual information.
Coding theory
Coding theory is one of the most important and direct applications of information theory. It can be subdivided into source coding theory and channel coding theory. Using a statistical description for data, information theory quantifies the number of bits needed to describe the data, which is the information entropy of the source.
- Data compression (source coding): There are two formulations for the compression problem:
- lossless data compression: the data must be reconstructed exactly;
- lossy data compression: allocates bits needed to reconstruct the data, within a specified fidelity level measured by a distortion function. This subset of Information theory is called rate–distortion theory.
- Error-correcting codes (channel coding): While data compression removes as much redundancy as possible, an error correcting code adds just the right kind of redundancy (i.e., error correction) needed to transmit the data efficiently and faithfully across a noisy channel.
This division of coding theory into compression and transmission is justified by the information transmission theorems, or source–channel separation theorems that justify the use of bits as the universal currency for information in many contexts. However, these theorems only hold in the situation where one transmitting user wishes to communicate to one receiving user. In scenarios with more than one transmitter (the multiple-access channel), more than one receiver (the broadcast channel) or intermediary "helpers" (the relay channel), or more general networks, compression followed by transmission may no longer be optimal. Network information theory refers to these multi-agent communication models.
Source theory
Any process that generates successive messages can be considered a source of information. A memoryless source is one in which each message is an independent identically-distributed random variable, whereas the properties of ergodicity and stationarity impose more general constraints. All such sources are stochastic. These terms are well studied in their own right outside information theory.
Rate
Information rate is the average entropy per symbol. For memoryless sources, this is merely the entropy of each symbol, while, in the case of a stationary stochastic process, it is
that is, the conditional entropy of a symbol given all the previous symbols generated. For the more general case of a process that is not necessarily stationary, the average rate is
that is, the limit of the joint entropy per symbol. For stationary sources, these two expressions give the same result.[10]
It is common in information theory to speak of the "rate" or "entropy" of a language. This is appropriate, for example, when the source of information is English prose. The rate of a source of information is related to its redundancy and how well it can be compressed, the subject of source coding.
Channel capacity
Communications over a channel—such as an ethernet cable—is the primary motivation of information theory. As anyone who's ever used a telephone (mobile or landline) knows, however, such channels often fail to produce exact reconstruction of a signal; noise, periods of silence, and other forms of signal corruption often degrade quality. How much information can one hope to communicate over a noisy (or otherwise imperfect) channel?
Consider the communications process over a discrete channel. A simple model of the process is shown below:
Here X represents the space of messages transmitted, and Y the space of messages received during a unit time over our channel. Let 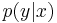 be the conditional probability distribution function of Y given X. We will consider
be the conditional probability distribution function of Y given X. We will consider 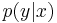 to be an inherent fixed property of our communications channel (representing the nature of the noise of our channel). Then the joint distribution of X and Y is completely determined by our channel and by our choice of
to be an inherent fixed property of our communications channel (representing the nature of the noise of our channel). Then the joint distribution of X and Y is completely determined by our channel and by our choice of 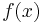 , the marginal distribution of messages we choose to send over the channel. Under these constraints, we would like to maximize the rate of information, or the signal, we can communicate over the channel. The appropriate measure for this is the mutual information, and this maximum mutual information is called the channel capacity and is given by:
, the marginal distribution of messages we choose to send over the channel. Under these constraints, we would like to maximize the rate of information, or the signal, we can communicate over the channel. The appropriate measure for this is the mutual information, and this maximum mutual information is called the channel capacity and is given by:
This capacity has the following property related to communicating at information rate R (where R is usually bits per symbol). For any information rate R < C and coding error ε > 0, for large enough N, there exists a code of length N and rate ≥ R and a decoding algorithm, such that the maximal probability of block error is ≤ ε; that is, it is always possible to transmit with arbitrarily small block error. In addition, for any rate R > C, it is impossible to transmit with arbitrarily small block error.
Channel coding is concerned with finding such nearly optimal codes that can be used to transmit data over a noisy channel with a small coding error at a rate near the channel capacity.
Capacity of particular channel models
- A continuous-time analog communications channel subject to Gaussian noise — see Shannon–Hartley theorem.
- A binary symmetric channel (BSC) with crossover probability p is a binary input, binary output channel that flips the input bit with probability p. The BSC has a capacity of
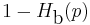 bits per channel use, where
bits per channel use, where 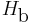 is the binary entropy function to the base 2 logarithm:
is the binary entropy function to the base 2 logarithm:
- A binary erasure channel (BEC) with erasure probability p is a binary input, ternary output channel. The possible channel outputs are 0, 1, and a third symbol 'e' called an erasure. The erasure represents complete loss of information about an input bit. The capacity of the BEC is 1 - p bits per channel use.
Applications to other fields
Intelligence uses and secrecy applications
Information theoretic concepts apply to cryptography and cryptanalysis. Turing's information unit, the ban, was used in the Ultra project, breaking the German Enigma machine code and hastening the end of WWII in Europe. Shannon himself defined an important concept now called the unicity distance. Based on the redundancy of the plaintext, it attempts to give a minimum amount of ciphertext necessary to ensure unique decipherability.
Information theory leads us to believe it is much more difficult to keep secrets than it might first appear. A brute force attack can break systems based on asymmetric key algorithms or on most commonly used methods of symmetric key algorithms (sometimes called secret key algorithms), such as block ciphers. The security of all such methods currently comes from the assumption that no known attack can break them in a practical amount of time.
Information theoretic security refers to methods such as the one-time pad that are not vulnerable to such brute force attacks. In such cases, the positive conditional mutual information between the plaintext and ciphertext (conditioned on the key) can ensure proper transmission, while the unconditional mutual information between the plaintext and ciphertext remains zero, resulting in absolutely secure communications. In other words, an eavesdropper would not be able to improve his or her guess of the plaintext by gaining knowledge of the ciphertext but not of the key. However, as in any other cryptographic system, care must be used to correctly apply even information-theoretically secure methods; the Venona project was able to crack the one-time pads of the Soviet Union due to their improper reuse of key material.
Pseudorandom number generation
Pseudorandom number generators are widely available in computer language libraries and application programs. They are, almost universally, unsuited to cryptographic use as they do not evade the deterministic nature of modern computer equipment and software. A class of improved random number generators is termed cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generators, but even they require external to the software random seeds to work as intended. These can be obtained via extractors, if done carefully. The measure of sufficient randomness in extractors is min-entropy, a value related to Shannon entropy through Rényi entropy; Rényi entropy is also used in evaluating randomness in cryptographic systems. Although related, the distinctions among these measures mean that a random variable with high Shannon entropy is not necessarily satisfactory for use in an extractor and so for cryptography uses.
Seismic exploration
One early commercial application of information theory was in the field seismic oil exploration. Work in this field made it possible to strip off and separate the unwanted noise from the desired seismic signal. Information theory and digital signal processing offer a major improvement of resolution and image clarity over previous analog methods.[11]
Miscellaneous applications
Information theory also has applications in gambling and investing, black holes, bioinformatics, and music.
See also
Applications
- Cryptanalysis
- Cryptography
- Cybernetics
- Entropy in thermodynamics and information theory
- Gambling
- Intelligence (information gathering)
- Seismic exploration
History
- Hartley, R.V.L.
- History of information theory
- Shannon, C.E.
- Timeline of information theory
- Yockey, H.P.
Theory
- Coding theory
- Detection theory
- Estimation theory
- Fisher information
- Information algebra
- Information asymmetry
- Information geometry
- Information theory and measure theory
- Kolmogorov complexity
- Logic of information
- Network coding
- Philosophy of Information
- Quantum information science
- Semiotic information theory
- Source coding
Concepts
- ban (information)
- Channel capacity
- Channel (communications)
- Communication source
- Conditional entropy
- Covert channel
- Decoder
- Differential entropy
- Encoder
- Information entropy
- Joint entropy
- Kullback-Leibler divergence
- Mutual information
- Pointwise Mutual Information (PMI)
- Receiver (information theory)
- Redundancy
- Rényi entropy
- Self-information
- Unicity distance
- Variety
References
- ^ F. Rieke, D. Warland, R Ruyter van Steveninck, W Bialek, Spikes: Exploring the Neural Code. The MIT press (1997).
- ^ cf. Huelsenbeck, J. P., F. Ronquist, R. Nielsen and J. P. Bollback (2001) Bayesian inference of phylogeny and its impact on evolutionary biology, Science 294:2310-2314
- ^ Rando Allikmets, Wyeth W. Wasserman, Amy Hutchinson, Philip Smallwood, Jeremy Nathans, Peter K. Rogan, Thomas D. Schneider, Michael Dean (1998) Organization of the ABCR gene: analysis of promoter and splice junction sequences, Gene 215:1, 111-122
- ^ Burnham, K. P. and Anderson D. R. (2002) Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, Second Edition (Springer Science, New York) ISBN 978-0-387-95364-9.
- ^ Jaynes, E. T. (1957) Information Theory and Statistical Mechanics, Phys. Rev. 106:620
- ^ Charles H. Bennett, Ming Li, and Bin Ma (2003) Chain Letters and Evolutionary Histories, Scientific American 288:6, 76-81
- ^ David R. Anderson (November 1, 2003). "Some background on why people in the empirical sciences may want to better understand the information-theoretic methods" (pdf). http://aicanderson2.home.comcast.net/~aicanderson2/home.pdf. Retrieved 2010-06-23.
- ^ Fazlollah M. Reza (1961, 1994). An Introduction to Information Theory. Dover Publications, Inc., New York. ISBN 0-486-68210-2. http://books.google.com/books?id=RtzpRAiX6OgC&pg=PA8&dq=intitle:%22An+Introduction+to+Information+Theory%22++%22entropy+of+a+simple+source%22.
- ^ Robert B. Ash (1965, 1990). Information Theory. Dover Publications, Inc.. ISBN 0-486-66521-6. http://books.google.com/books?id=ngZhvUfF0UIC&pg=PA16&dq=intitle:information+intitle:theory+inauthor:ash+conditional+uncertainty.
- ^ Jerry D. Gibson (1998). Digital Compression for Multimedia: Principles and Standards. Morgan Kaufmann. ISBN 1558603697. http://books.google.com/books?id=aqQ2Ry6spu0C&pg=PA56&dq=entropy-rate+conditional#PPA57,M1.
- ^ The Corporation and Innovation, Haggerty, Patrick, Strategic Management Journal, Vol. 2, 97-118 (1981)
The classic work
- Shannon, C.E. (1948), "A Mathematical Theory of Communication", Bell System Technical Journal, 27, pp. 379–423 & 623–656, July & October, 1948. PDF.
Notes and other formats. - R.V.L. Hartley, "Transmission of Information", Bell System Technical Journal, July 1928
- Andrey Kolmogorov (1968), "Three approaches to the quantitative definition of information" in International Journal of Computer Mathematics.
Other journal articles
- J. L. Kelly, Jr., Saratoga.ny.us, "A New Interpretation of Information Rate" Bell System Technical Journal, Vol. 35, July 1956, pp. 917–26.
- R. Landauer, IEEE.org, "Information is Physical" Proc. Workshop on Physics and Computation PhysComp'92 (IEEE Comp. Sci.Press, Los Alamitos, 1993) pp. 1–4.
- R. Landauer, IBM.com, "Irreversibility and Heat Generation in the Computing Process" IBM J. Res. Develop. Vol. 5, No. 3, 1961
Textbooks on information theory
- Claude E. Shannon, Warren Weaver. The Mathematical Theory of Communication. Univ of Illinois Press, 1949. ISBN 0-252-72548-4
- Robert Gallager. Information Theory and Reliable Communication. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1968. ISBN 0-471-29048-3
- Robert B. Ash. Information Theory. New York: Interscience, 1965. ISBN 0-470-03445-9. New York: Dover 1990. ISBN 0-486-66521-6
- Thomas M. Cover, Joy A. Thomas. Elements of information theory, 1st Edition. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 1991. ISBN 0-471-06259-6.
- 2nd Edition. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 2006. ISBN 0-471-24195-4.
- Imre Csiszar, Janos Korner. Information Theory: Coding Theorems for Discrete Memoryless Systems Akademiai Kiado: 2nd edition, 1997. ISBN 963-05-7440-3
- Raymond W. Yeung. A First Course in Information Theory Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, 2002. ISBN 0-306-46791-7
- David J. C. MacKay. Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003. ISBN 0-521-64298-1
- Raymond W. Yeung. Information Theory and Network Coding Springer 2008, 2002. ISBN 978-0-387-79233-0
- Stanford Goldman. Information Theory. New York: Prentice Hall, 1953. New York: Dover 1968 ISBN 0-486-62209-6, 2005 ISBN 0-486-44271-3
- Fazlollah Reza. An Introduction to Information Theory. New York: McGraw-Hill 1961. New York: Dover 1994. ISBN 0-486-68210-2
- Masud Mansuripur. Introduction to Information Theory. New York: Prentice Hall, 1987. ISBN 0-13-484668-0
- Christoph Arndt: Information Measures, Information and its Description in Science and Engineering (Springer Series: Signals and Communication Technology), 2004, ISBN 978-3-540-40855-0
Other books
- Leon Brillouin, Science and Information Theory, Mineola, N.Y.: Dover, [1956, 1962] 2004. ISBN 0-486-43918-6
- James Gleick, The Information: A History, a Theory, a Flood, New York: Pantheon, 2011. ISBN 978-0375423727
- A. I. Khinchin, Mathematical Foundations of Information Theory, New York: Dover, 1957. ISBN 0-486-60434-9
- H. S. Leff and A. F. Rex, Editors, Maxwell's Demon: Entropy, Information, Computing, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ (1990). ISBN 0-691-08727-X
- Tom Siegfried, The Bit and the Pendulum, Wiley, 2000. ISBN 0-471-32174-5
- Charles Seife, Decoding The Universe, Viking, 2006. ISBN 0-670-03441-X
- Jeremy Campbell, Grammatical Man, Touchstone/Simon & Schuster, 1982, ISBN 0-671-44062-4
- Henri Theil, Economics and Information Theory, Rand McNally & Company - Chicago, 1967.
External links
- alum.mit.edu, Eprint, Schneider, T. D., "Information Theory Primer"
- ND.edu, Srinivasa, S. "A Review on Multivariate Mutual Information"
- Chem.wisc.edu, Journal of Chemical Education, Shuffled Cards, Messy Desks, and Disorderly Dorm Rooms - Examples of Entropy Increase? Nonsense!
- ITsoc.org, IEEE Information Theory Society and ITsoc.org review articles
- Cam.ac.uk, On-line textbook: "Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms" by David MacKay - giving an entertaining and thorough introduction to Shannon theory, including state-of-the-art methods from coding theory, such as arithmetic coding, low-density parity-check codes, and Turbo codes.
- UMBC.edu, Eprint, Erill, I., "A gentle introduction to information content in transcription factor binding sites"
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
![H(X) = \mathbb{E}_{X} [I(x)] = -\sum_{x \in \mathbb{X}} p(x) \log p(x).](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/4f0080f2c78d5b39d6f8ce8dfa076f8e.png)
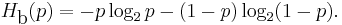
![H(X, Y) = \mathbb{E}_{X,Y} [-\log p(x,y)] = - \sum_{x, y} p(x, y) \log p(x, y) \,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/0a2e66566a03512cb500db06175aa4dd.png)
![H(X|Y) = \mathbb E_Y [H(X|y)] = -\sum_{y \in Y} p(y) \sum_{x \in X} p(x|y) \log p(x|y) = -\sum_{x,y} p(x,y) \log \frac{p(x,y)}{p(y)}.](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/20aacd9fd5d717de99c4656d983c9484.png)
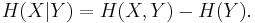
![I(X;Y) = \mathbb{E}_{X,Y} [SI(x,y)] = \sum_{x,y} p(x,y) \log \frac{p(x,y)}{p(x)\, p(y)}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/391eeed3480f23a5303f87bede98769a.png)
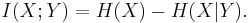
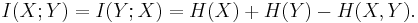
![I(X;Y) = \mathbb E_{p(y)} [D_{\mathrm{KL}}( p(X|Y=y) \| p(X) )].](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8c9a47120e2cf50d9600cbdfe5f3907f.png)